No products in the cart.
The Gut: More Than Just Digestion
Traditionally seen as the digestive system’s headquarters, the gut is now recognized as a complex ecosystem teeming with trillions of microorganisms. This vast community of bacteria, known as the gut microbiota, influences not only digestion but also immune function, hormone regulation, and surprisingly, our brain health.
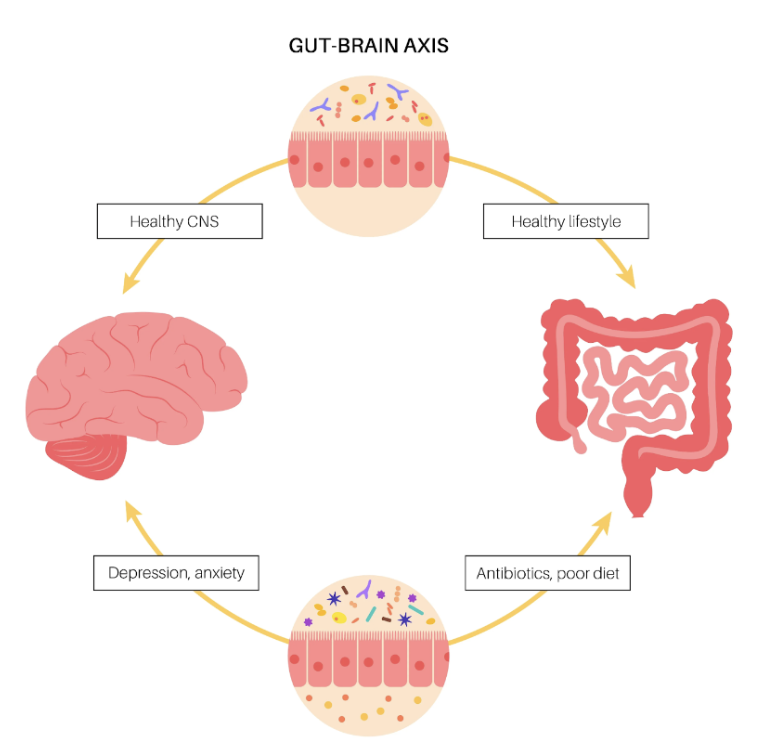
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Two-Way Street
The gut and the brain communicate bidirectionally through a highway known as the gut-brain axis. Signals flow in both directions, with the gut microbiota impacting brain function and the brain influencing gut activity. This intricate connection highlights the potential for digestive health to impact our emotional well-being.
Mood and Microbes: The Impact on Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a link between the gut microbiota and conditions such as anxiety, depression, and stress. Specific strains of gut bacteria are associated with the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play pivotal roles in regulating mood.
Inflammation and Cognitive Function
Chronic inflammation, often triggered by an imbalanced gut, has been implicated in cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. A healthy gut helps maintain a balanced immune response, reducing the risk of inflammation-related cognitive issues.
The Role of Nutrition and Lifestyle
Nurturing a diverse and thriving gut microbiota requires attention to diet and lifestyle. Consuming a variety of fiber-rich foods, prebiotics, and probiotics can foster a harmonious gut environment, ultimately benefiting mental health.
Stress, the Gut, and Resilience
Stress, whether emotional or physical, can disturb the balance of the gut microbiota. Conversely, a disrupted gut can amplify stress responses. Learning stress management techniques and prioritizing gut health can create a positive feedback loop of resilience.
Nurturing Your Gut-Brain Connection
Here are practical steps to nurture your gut-brain connection:
Diverse Diet: Include a range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods to provide nourishment for your gut microbes.
Hydration: Stay well-hydrated to support digestion and the transport of nutrients to your brain.
Mindful Eating: Eat mindfully, paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, and enjoying your meals in a relaxed environment.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise can promote gut diversity and improve mood by releasing endorphins.
Stress Reduction: Engage in stress-reduction practices like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to calm the mind and gut.
As the science behind the gut-brain connection continues to unfold, it’s clear that nurturing your gut health is a pivotal step toward enhancing your mental well-being. Regardless of age, investing in a balanced diet, stress management, and a holistic lifestyle can pave the way for improved mood, cognitive function, and emotional equilibrium. By embracing this symbiotic relationship between your gut and brain, you’re taking proactive steps towards a healthier and happier life.