No products in the cart.
Health Guides
Digestive and Gut Health
Understanding Digestive Enzymes
You’ve probably heard of digestive enzymes, but do you really know what they are or why they’re so important?

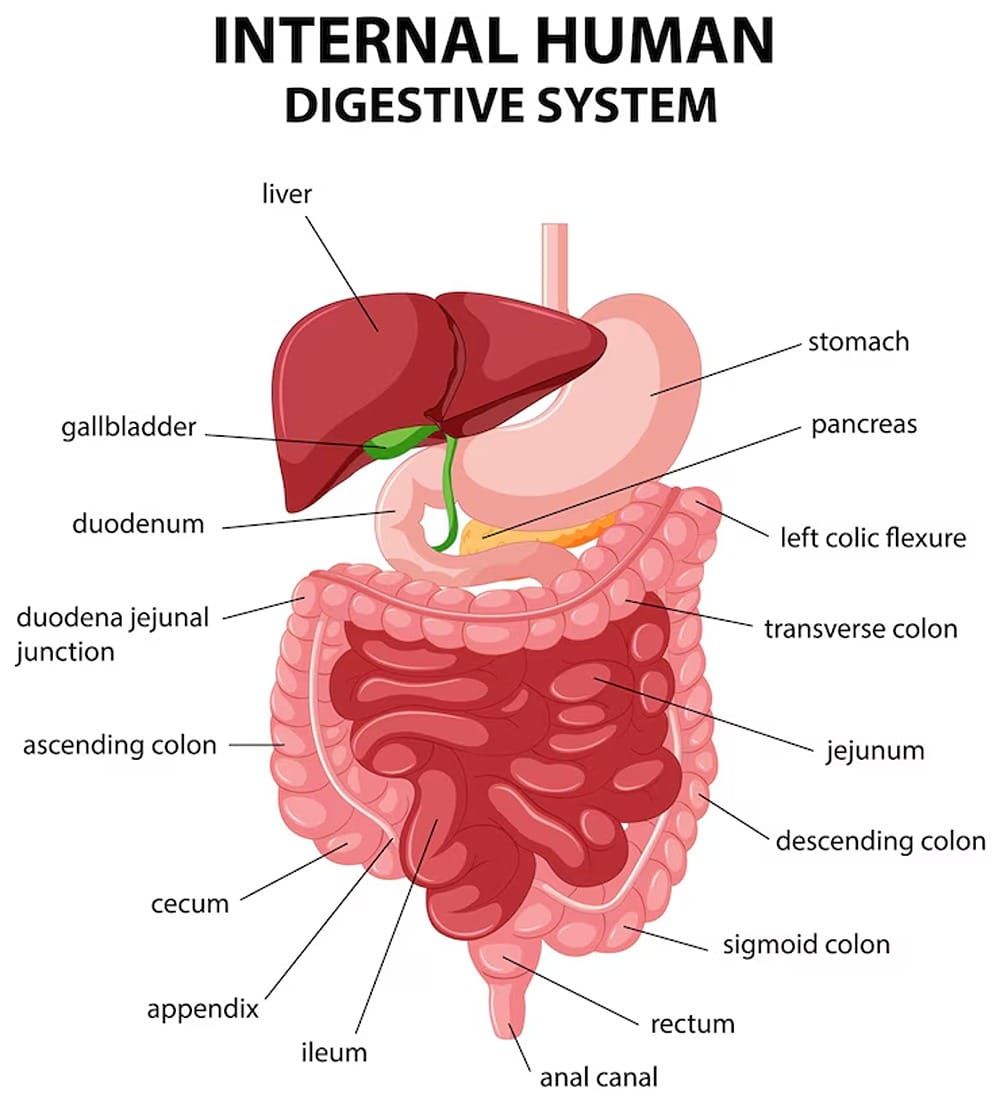
Internal Human Digestive System
Understanding Digestive Enzymes and Their Role in Your Body
Digestive enzymes are special proteins that play a crucial role in breaking down the food you eat into essential nutrients your body needs to function. For example, when you enjoy a pack of nasi lemak, the food travels down to your stomach and eventually reaches the duodenum, the first section of your small intestine. Here, your pancreas steps in by producing and releasing digestive enzymes into the duodenum. These enzymes work to break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, allowing your body to absorb nutrients effectively as the food moves through the small intestine.
Types of Digestive Enzymes
Your body naturally produces these enzymes in the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine. There are three main types, each with a specific function:
- Amylase: Breaks down carbohydrates (like rice, pasta, and bread) into simple sugars.
- Protease: Breaks down proteins (like meat, eggs, and beans) into amino acids.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats (like oils, butter, and cheese) into fatty acids and glycerol.
These enzymes ensure that digestion happens efficiently, making it possible for your body to absorb the nutrients it needs. Without them, the digestive process would be slower and less effective, potentially causing discomfort or bloating.
What Happens When Your Body Lacks Digestive Enzymes?
When your body doesn’t produce enough digestive enzymes, issues like indigestion, bloating, and food sensitivities can arise. Without adequate enzymes, your digestive system struggles to break down food, leading to discomfort and poor nutrient absorption.
For those who frequently experience digestive problems, such as feeling bloated after meals or having trouble digesting protein-heavy dishes, enzyme supplements can be a game-changer. These supplements provide additional enzymes to support the natural digestive process, helping you feel more comfortable and improving nutrient absorption.
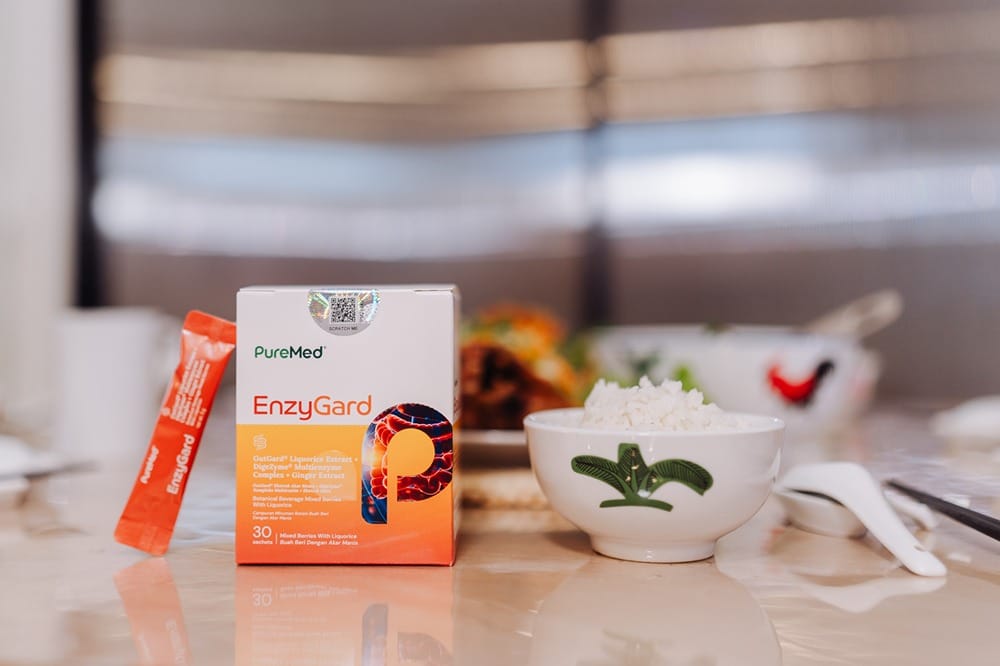

EnzyGard: 3in1 Natural Solution for Digestive Discomfort
Do you experience:
- Bloating and gas?
- Persistent bad breath?
- Upset stomach, heartburn, or indigestion?
- Discomfort after meals?
- Occasional nausea and vomiting?
If so, you can try EnzyGard to ease these digestive discomfort!
Why Choose EnzyGard?
EnzyGard is specifically designed to:
- Improve digestion.
- Promote Gut Motility.
- Reduce Gut Inflammation.
- Soothe digestive discomfort.
- Protect the stomach’s mucosal lining from H. Pylori’
Key Ingredients:
- GutGard®: A clinically researched, flavonoid-rich natural bioactive that soothes digestive discomfort and protects the stomach lining [1].
- DigeZyme®: A carefully formulated blend of five digestive enzymes that aid in breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, reducing digestive discomfort [2].
- Ginger Extract: Supports gut health, alleviates nausea, and provides gentle relief from daily digestive discomfort [3].
Digestive enzymes play a vital role in nutrition and overall health by helping your body break down food and absorb essential nutrients. Without sufficient enzymes, you may experience uncomfortable symptoms, food intolerances, or even nutrient deficiencies.
If you’re struggling with digestive discomfort, consider EnzyGard—a gentle, natural solution with digestive enzymes, designed to support digestion and improve nutrient absorption. Talk to a healthcare professional about your symptoms or click here or the link below to learn how
EnzyGard can complement your journey to better digestive health.
EnzyGard
Reference:
- Natural Remedies for Human Health. (n.d.). GutGard. Retrieved January 21, 2025, from https://naturalremedieshumanhealth.com/gutgard/
- DigeZyme. (n.d.). DigeZyme—The multi-enzyme complex. Retrieved January 21, 2025, from https://digezyme.com/
- Foshati, S., Poursadeghfard, M., Heidari, Z., & Rostami, R. (2023). The effects of ginger supplementation on common gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, 23(1), 383. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-023-04227-x
Recommended Articles
Join Our Newsletter
Sign up now to receive the latest news and promotions.
Shop
Learn
Support
KKLIU: 2136/2022 © 2023 PureMed. All rights reserved.

