No products in the cart.
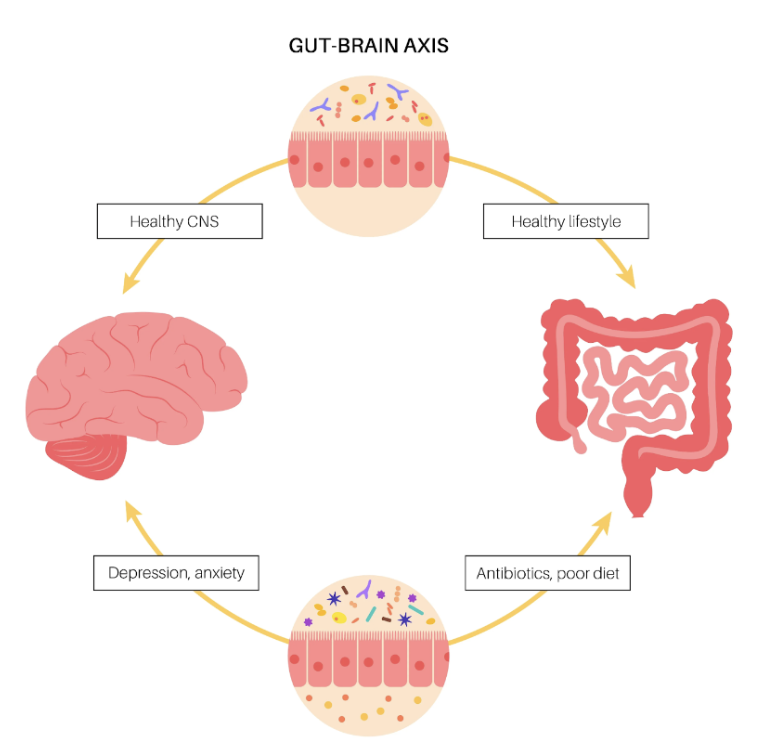
Gut is our second immune system. 80% of our immune defense is located in our gut and a balanced microbiota and enough of good bacteria is important for a well-functioning immune system. The good bacteria educate the immune system, making it ready to fight unwelcome invaders like bad bacteria and toxins. To achieve a healthy balance the good bacteria need to outnumber the bad with ten to one.
If bad bacteria for some reason start to exceed it may lead to an imbalance in the digestive system, called dysbiosis. Dysbiosis may cause problems like diarrhoea, constipation, bloating, temporary stomach pain and leaky gut.